The Evolving Volunteer Force
While the tactics of fighting wars have evolved, military structure and methods of evaluating personnel have lagged behind. What steps can the U.S. military take to ensure that it can move as quickly as the next generation of warfare?
 U.S. Marines jump from the back of a U.S. Air Force C-130 Hercules. (Staff Sergeant Michael Washburn/U.S. Air Force)
U.S. Marines jump from the back of a U.S. Air Force C-130 Hercules. (Staff Sergeant Michael Washburn/U.S. Air Force)
We miss something vital when our minds turn to visions of advanced weapons, technologies, and scientific breakthroughs whenever we consider the 21st century military. As important as those elements are, they are not the key to greatness. The key is people and nothing else.
Think about the super-teams in the NBA or NFL, loaded with the most expensive “weapons” that money can buy. Those organizations often lose to well-coached teams that play seamlessly as one.
Volunteer Force?
Similarly, people are the key to a successful 21st century military. That’s why there must be progress in evolving the volunteer force, especially with millennials joining the services. Managing the new generation of millennials will offer unique challenges, but that’s a secondary concern if the core principles are right.
The status quo is not an option. If the task is merely to resist the growth of a suffocating bureaucracy, we have already lost. As two recent defense secretaries, Ash Carter and Robert Gates, made clear, the existing personnel bureaucracy is arguably the top threat to readiness facing our armed forces.
When the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, I was a butterbar – a newly-commissioned second lieutenant – heading to the Pacific for my first active-duty assignment. One mentor joked that communist central planning was dead all around the world, except for three last holdouts: “Havana, Harvard, and the Pentagon’s personnel commands.”
Despite the implementation of the all-volunteer force in 1973, control of promotions and assignments became more centralized. In 1980, Congress passed legislation that required each service to follow the same promotion timetables with little regard for merit.
The immediate problem is not that millennials are different, rather that warfare is different. Faster. The Pentagon is different, too. Slower. Although millennials volunteering for service are extraordinarily talented and agile, the military personnel bureaucracies are rigid. That Achilles heel will lose wars. Cyberwars, for one, but counterinsurgencies, too.
The immediate problem is not that millennials are different, rather that warfare is different. Faster. The Pentagon is different, too. Slower.
All service members are required to rotate to new jobs, usually at a different base far away, every 18 to 24 months. Up-or-out is the mantra.
Matching troops to billets is driven by elaborate manpower requirements. Establishing those requirements is a nightmare of central planning, impossible to do well in a world of constant change.
For example, the 2015 National Security Strategy considers cyber threats one of the top national security challenges. Yet a decade ago, cyber threats were not even mentioned. There were no cyber billets, projections for billets, or plans to grow the right talent.
It wasn’t always this way. During World War II, the Army and Navy had different force structures and unique personnel systems. That kind of flexibility is impossible now. I’ve spoken with flag officers in charge of personnel for the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, and Air Force, as well as hundreds of combat veterans. They all say reform of some kind is needed.
Fortunately, many top admirals and generals are putting new procedures in place. But key laws make many needed reforms off limits.
My forthcoming book, Total Volunteer Force, offers specific recommendations but they fall into three general areas. First, performance evaluations must be improved. Second, job-matching must be decentralized. Third, compensation must be reformed to reward skills instead of seniority.
First, performance evaluations must be improved. Second, job-matching must be decentralized. Third, compensation must be reformed to reward skills instead of seniority.
Rangers Lead the Way
 U.S. Army Rangers with the 1st Battalion, 75th Ranger Regiment, train at Hunter Army Airfield, Ga., June 2, 2014. (Army Specialist Coty Kuhn/Department of Defense)
U.S. Army Rangers with the 1st Battalion, 75th Ranger Regiment, train at Hunter Army Airfield, Ga., June 2, 2014. (Army Specialist Coty Kuhn/Department of Defense)
The Defense Department has 660 Special Operational Force teams, three Army Ranger battalions, and a total of 66,000 personnel assigned to Special Operations Command. These are arguably the most elite warriors of all time, and it might be worth considering how.
Traditional military units are managed using a strict hierarchy, known as the chain of command. This structure, and the top-down nature of military performance evaluations, has a predictable effect on behavioral incentives.
Many officers advance their careers by focusing excessively on making a good impression on their rating commander while being otherwise toxic toward subordinates and peers. Unfortunately, rapid job rotations every two years make it hard to identify toxic leaders before they have already moved on.
In contrast, the U.S. Army Ranger School uses peer evaluations as an integral part of the training. Individuals are routinely removed if rated poorly by a wide group of peers in the same class. Students offer — and receive — peer evaluations three times during the course.
The simple process involves rank-ordering fellow students and answering two basic questions: “Would you go to war with this person?” and “Would you share a foxhole with this person?” If a student is “peered out” with a majority of negative ratings, that individual is recycled to a different platoon and given a second chance.
The consequences of “Ranger-peering” are a central shaping event in the lives of elite Army soldiers. They are widely cited as a key in promoting excellence. But peering plays no role in standard Army performance management.
Instead, the Army, Navy, and especially the Air Force are plagued by highly-inflated, uninformative top-down evaluation systems. Bob Gates spends four pages of his new book, A Passion for Leadership, describing how “deeply flawed” these are, with the chilling observation that the mentally-disturbed officer who killed 13 people on a rampage at Fort Hood had received sterling performance evaluations.
The Marine Corps stands apart from the other services with its world-class fitness reports. Not only are the quantitative assessments useful in identifying individual talents, the comment blocks offer valuable feedback. Yet even the Marines neglect peer and subordinate feedback. This is a missed opportunity.
To improve talent management, the services should immediately implement a better evaluation system that identifies unique skills and includes Ranger-like peer evaluations. Along with serving as the building block for improved promotions and assignments, these would provide the kind of personal attention that millennials reportedly thrive on.
Command Authority
Two surprising facts about the U.S. force posture in recent years stand out.
First, the percentage of the population serving on active duty is lower today than at any time in the modern era. The figure is 0.43 percent, to be exact. Second, fewer deployed U.S. troops are based overseas relative to the world population than at any time since 1950. These two facts establish an unmistakable long-term trend: the strategic withdrawal of U.S. forces from the world.
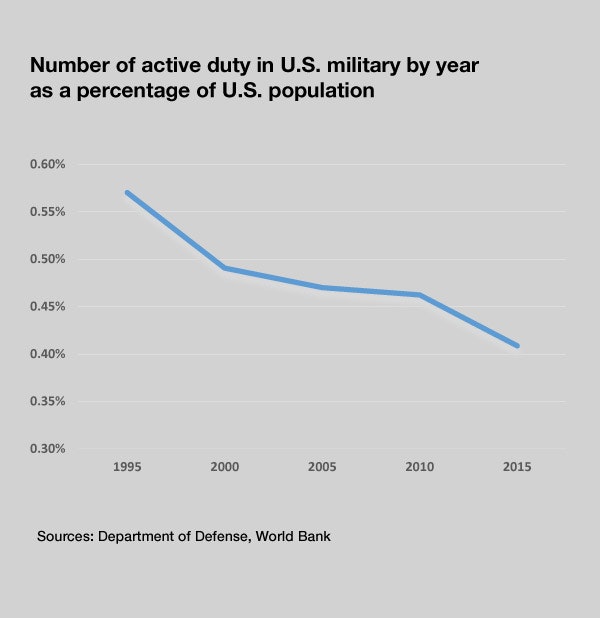
The upside of this smaller force is that the services can be very selective. Contrary to many false perceptions, today’s young veterans are more educated and more talented than their civilian peers. Indeed, combat veterans who leave the service have a far lower unemployment rate than comparable civilians, and earn higher average paychecks than nonveterans.
What makes millennials unique is that they have been raised from birth in the internet era. Many of this year’s enlistees were born in 1998, the same year Google was born. This generation grew up connected, and the implication for personnel policy is that they are far more aware of alternative work opportunities out of uniform.
 A 380th Expeditionary Aircraft Maintenance Squadron maintainer begins an E-3 Sentry post-flight inspection after a sortie in support of Combined Joint Task Force-Operation Inherent Resolve at an undisclosed location in Southwest Asia, Jan. 12, 2017. (Senior Airman Tyler Woodward/U.S. Air Force)
A 380th Expeditionary Aircraft Maintenance Squadron maintainer begins an E-3 Sentry post-flight inspection after a sortie in support of Combined Joint Task Force-Operation Inherent Resolve at an undisclosed location in Southwest Asia, Jan. 12, 2017. (Senior Airman Tyler Woodward/U.S. Air Force)
No longer can the armed forces treat young troops as indentured servants with few alternatives. Indeed, one of the top frustrations of separating service members and their spouses is a sense that they have so little control over their military careers.
Amazingly, commanders in today’s military also have little control. For example, you might be the captain of a Navy destroyer with hundreds of sailors under your command, but you have no command authority over who serves on your ship.
No longer can the armed forces treat young troops as indentured servants with few alternatives. Indeed, one of the top frustrations of separating service members and their spouses is a sense that they have so little control over their military careers.
This situation led Senator John McCain to ponder at a 2015 Senate hearing: “We should ask whether we should give commanders greater discretion to build a staff with the specialists and experts they need in the right positions. Commanders are likely better able to assess their needs than bureaucrats in the personnel system.”
I believe the problem of sexual assault in the military is, in fact, directly linked to the lack of authority commanders have over hiring. The formalized process run through faceless bureaucracies has no idea if a soldier is sketchy, sexist, or mentally unstable. If a person meets minimum standards and has committed no crime, they meet the lowest common denominator. Our troops deserve better.
Anyone in the military with a mid-level commander rank (lieutenant colonel in the Army, Marines, and Air Force or commander in the Navy) and above should be given final authority on who serves in his or her unit. Personnel centers, rather than selecting one person per billet, will provide a slate of no fewer than three candidates for the unit commander to interview.
Paying for Wrong Kind of Security
For most of its history, our military was haunted by seniority. Today’s seniority problem is milder, but it is more engrained in the compensation structure than ever before.
Despite a new “blended” retirement system for service members who will join the ranks in 2018, a defined benefit that vests at exactly 20 years of a service remains in place. Leave before year 20 and get nothing, but any day after 20 and you immediately get a monthly payment worth half of your base pay.
In the “new” system, that payment is 40, not 50, percent, but the cliff remains. Research shows this 20-year “cliff vesting” creates a bubble of personnel that immediately deflates at the 21st year of service.
Unfortunately, the U.S. military is saddled with a legacy of rigid base pay tables, calculated on two dimensions since at least 1949: rank and cumulative time in service. Sadly, tenure pays more than rank.
The use of tenure-base pay is an anachronism of a day when personalized algorithms that factor in occupation, location, and skill were technologically impossible. Those days are gone. Indeed, the Navy used skill-based pay during the century after the nation was founded. It should be allowed to do so again.
The good news is these reforms make sense not just to us, but they also make sense to congressional leaders on both sides of the aisle, such as Democratic Senator Jack Reed and GOP Representative Mac Thornberry. They make sense to the heads of personnel policy in each of the services, too. There’s only one enemy in this battle: bureaucratic momentum. And I predict it will lose.
The good news is these reforms make sense not just to us, but they also make sense to congressional leaders on both sides of the aisle. There’s only one enemy in this battle: bureaucratic momentum.
-
Previous Article Warriors at Home: Military Families Face Challenges An Essay by Sheila Casey, Chair, Blue Star Families
-
Next Article Veterans Can Fill the Skills Gap An Essay by Corporal Jeffrey Cleland, USMC (Ret.), Manager, Military Service Initiative, George W. Bush Institute, and Laura Collins, Deputy Director, Economic Growth, George W. Bush Institute

